
This is an early AMD Athlon 64 engineering sample. It's made in the 19th week of 2002 and it's official name according to the motherboard is Athlon HX. A quick Google reveals that the 'HX' name is (or was about to be) used for dual Athlon systems. As the original motherboard that came with this CPU is called 'AMD Solo 5' I suspect that this S754 CPU is capable of symmetric multi processing (SMP). For your information: a production dual S754 system has never been produced and only one engineering sample motherboard (AMD Stretto), without CPU's and BIOS, has been spotted in the wild.
My Athlon HX 1400 came along with an AMD Solo 5 motherboard. This motherboard has a first revision (A0; Thor) HyperTransport I/O Hub and second revision (A1; Lokar) HyperTransport AGP3.0 graphics tunnel chipset. Because this is pre-production (and early) hardware it's sometimes difficult to get the system going. Memory support is somewhat limited so I ran this system with one 512MB module that ran at 126MHz with CL2.5 latencies, or with 2x256MB DDR333 modules (Hynix) or with just one 256MB dual-sided DDR266 (Hynix) module. Also this CPU is not compatible with regular moterboards: I tried booting it ASUS K8V with VIA chipset but it doesn't start. It also works the other-way around: a production Athlon 64 3200+ (1MB, ClawHammer) doesn't work in the Solo 5 engineering sample motherboard. I think you will have better luck running this CPU in motherboards with the AMD-8111 chipset.
My AMD Solo 5 motherboard has the following BIOS ID String: 07/29/2002-AMDK8-SMC61W4-ASLAX1-00, ASLAX1-2
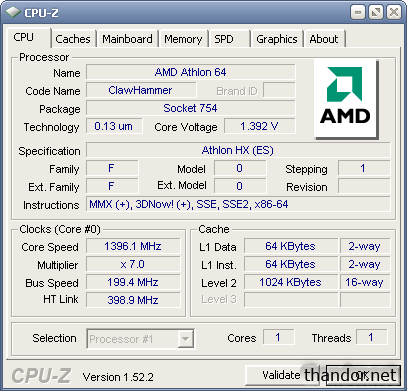
This is how it looks in CPUz:
To put this CPU in a timeframe I've been searching for news items of the Athlon 64 which also includes a part of the Opteron and Athlon 64 FX-51 because they are based on the same core.
February 2002
References of the AMD Solo 2 found.
6 May 2002
This CPU and AMD Solo 5 motherboard.
12 and 14 December 2002
At that time some benchmarks of an 1.2GHz Athlon 64 were published. The results can be found here. This meant that AMD was getting it's Athlon 64 ready and had working samples.
31 December 2002
On the very last day of 2002 some documents were found showing a diagram that spoke about Core 0 and Core 1 indicating that AMD was already designing the processor with dual-core in mind. AMD's dual-core processors were released in August 2005.
8 January 2003
The clockfrequencies and ratingsystem of the Athlon 64 is known. It's suggested to be 1,6GHz for 2800+, 1,8GHz for 3100+, 2,2GHz for 3400+ and 2,4GHz for 3700+ L2-cache sizes remain unknown.
27 January 2003
New benchmarks of the Athlon 64 with 256KB L2-cache. At the time it was called 'ClawHammer' but it was already known that 'Paris' should be the codename for the 256KB cores. Eventually 'Paris' was the codename for the 130nm Sempron on S754. The Athlon 64 that was benchmarked was probably running at 1400MHz with HT800. Performance was not impressive as the Athlon 64 had problems keeping up with the Athlon XP 2200+ and Pentium 4 2,26GHz. Performance of the motherboard was bad as Quake 3 didn't run faster than an Athlon XP 1400MHz (1600+).
31 January 2003
The launch of the Athlon 64 has been postponed but the launch of the Athlon XP 'Barton' and the Opteron has been confirmed. 10 February for the 512KB L2-cache Athlon XP (Barton) and 22 April for the Opteron running at 1,4GHZ, 1,6GHz and 1,8GHz.
20 February 2003
It's getting closer to the launch of the first K8 processor (Opteron and Athlon 64 share the same K8 technology) as AMD demonstrates an Athlon 64 notebook and quad Opteron system.
13 April 2003
The introduction of the Opteron is close and AMD doesn't want a paper-launch. To have the products ready for sale at the release the distributors already have Opterons in storage.
20 April 2003
Performance review of the Athlon 64 2800+ by X-Bit Labs. They laid hands on a B0 engineering sample running at 1,6GHz with 1MB L2-cache. It seems that AMD changed the Athlon 64 2800+ slightly because the production model runs at 1,8GHz and has 512KB L2-cache.
22 April 2003
The Opteron was launched and reviews pop up.
19 June 2003
Rumors are that the Athlon 64 on socket 939 will have a dual-channel memory controller in 2004.
20 June 2003
The Athlon 64 will be launched in September 2003; not August. At this moment there are also rumors that the new Pentium 4 'Prescott' is dealing with heat problems. That's true as my Pentium 4 520 engineering sample dated 44th week of 2003 uses quite a lot of energy.
29 June 2003
Someone overclocked the Opteron 242. Increasing the HyperTransport bus is difficult as 10MHz (210MHz in total) causes 3DMark to crash. Without GPU benchmarks the HT goes up to 220MHz so this indicates that the AGP bus is not fixed and thus overclocked as well. Apparently the chipset is able to reach higher frequencies without problems.
8 July 2003
The official release date of the Athlon 64 is known: 22 September 2003.
30 July 2003
Benchmarks of the Opteron using an ASUS SK8N nForce3 motherboard are published.
5 August 2003
The rating of the Athlon 64-FX is known. The models are 51, 53 and probably 55. This CPU is going to be the fastest desktop/enthusiast Athlon 64 AMD is going to release at 22 September 2003. It will use the same socket as the Opteron (S940) and also need Registered DDR-SDRAM indicating that the FX is technically an Opteron with unlocked multiplier.
22 August 2003
The Athlon 64 will be launched at 23 September (dates keep changing, first 22 September was the release date) with a single-channel DDR memory controller on socket S754. The fastest normal Athlon 64 will run at 2GHz and has a rating of 3200+. It's price tag will be 399 dollar. At the same time the Athlon 64-FX 51 will be launched using socket 940 with dual-channel memory controller for 700 dollar. The 2,2GHz Athlon 64 (3400+) will be introducted later.
3 September 2003
Benchmark results of the Athlon 64 FX-51 are known. The CPU should be able to beat the Pentium 4 'Northwood' running at 3.2GHz.
12 September 2003
The soon to be released Athlon 64 FX-51 is being overclocked but results are dissapointing. 2,3GHz on air and 2,48GHz using advanced cooling (Prometeia) which is marginal as the stock clock frequency is already 2,2GHz! More details aren't available because of a non disclosure agreement (NDA).
19 September 2003
Because AMD will release the Athlon 64 in a few days the Athlon 64 3200+ is already available for suppliers.
23 September 2003
AMD launches the Athlon 64 3200+ and Athlon 64 FX-51. First reviews appear on the Internet indicating the new processor is doing well. > Read more






