| The first processor with x86 architecture (which is still used today). The 8086 is a 16-bit processor with 16-bit data bus. It does not incorporate a co-processor, but an additional mathematical processor can be placed next to the 8086 for floating point calculations. The original 8086 was clocked at 4,77MHz, but faster versions we're clocked at 9MHz. Many chip makers manufactured a 8086, and some even enhanced it. For example the Nec V20 runs faster because it is based on the 80186 instruction set which shares characteristics with the 286. The right photo shows a 'die'-shot of the 8086. | 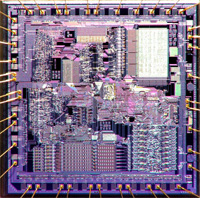 |
A nice looking 8086 CPU! The early chips were sometimes white with gold plated pins. In the late 80'ies more and more chips were housed in black plastic packaging without the gold plated pins.
This particular CPU has been manufactured in the 34th week of 1986. It is an Intel-design but built bij Fujitsu. Fujistu was one of the (many) second suppliers of Intel 8086 CPU's. These 'copies' of chips exist due to a requirement of IBM to have more than one supplier available for their systems.
The 8086-1 is rated to run at 10MHz. However, in many cases it was run at 8MHz since 8MHz is the maximum official frequency for the ISA-bus. Systems that run at 10MHz essentially overclock the ISA-bus and thus ISA-cards.
Chips marked 8086-2 are rated 8MHz and without marking are often the original ones at 4.77MHz. > Read more
Just like [iurl=https://thandor.net/object/994]this NEC V30[/url] but a few years newer and instead of a printed text on top it has engraved text. > Read more
Most XT-based systems are equipped with a 8088 class CPU or clone. Several other systems do their maths with the NEC V20 (a drop-in compatible CPU with the 8088) and older, more expensive, systems use the first classic 8086 CPU. The latter can also be swapped with a NEC counterpart: the NEC V30. Because most XT's were build around the 8088 CPU, the 8086 and V30 are somewhat uncommon these days.
The difference between the 8088/V20 and 8086/V30 is the external databus. 8086/V30 has an 16-bit external database for faster memory access. The 8088/V20 is basically the same but with half the datapins (thus 8-bit).
The NEC V20 is a reliable, cool running CPU that runs somewhat faster than the original 8088. I always wondered what a NEC V30 would do: I benchmarked it and it runs great! Even at 8MHz it surpasses the 10MHz TurboXT V20! It seems that the 16-bit bus really makes a difference with the NEC V30 ![]() . > Read more
. > Read more
It took a while to find a working 8086 system (got mine in an IBM 8530). Nowadays a working 8086 is getting scarce and most things that are being sold in the XT-class are 8088's.
The difference between the 8086 and 8088 is small; 8086 has an 16-bit external bus instead of 8-bit for the 8088. The 8088 is actually a cut-down version of the 8086 to reduce costs in motherboards. After all an 8-bit bus on a motherboard is cheaper. Internally both CPU's run at the same speed but accessing components on the external bus can be slightly faster on the 8086. Despite the small difference between the 8086 and 8088 you cannot interchange these chips; never run an 8088 chip in an 8086 motherboard!
I always wondered how an 8086 would perform compared to a 8088. In general you barely notice any difference (a cheaper NEC V20 is even faster on the DOS-prompt). In the DOSBench benchmark the 8086 is slightly ahead on the 8088. See benchmarks below showing 8 points for 5MHz 8088, 16 points for an 8MHz 8088, 18 points for the 8MHz 8086 and 22 points for an 8MHz NEC V20. The TurboXT, with an 10MHz NEC V20, is in the lead with 27 points. > Read more
Faster version of the original 8086. The CPU runs at 8MHz and so does the system bus. As far as I know all the 8MHz systems can run at 4.77MHz by disabling the turbo mode. This is usually done by pressing the turbo button or by press a certain key-combination (like CTRL ALT -) > Read more
This processor was manufactured in 1984. It runs at 4.77MHz and is notable as the processor used in the IBM PC PS/2 Model 30 and other compatibles/clones from that era. The first 8086 was introduced in 1978 and was sold for quite some time. Eventually most XT's were equipped with 8088 processors due to a less complex, 8-bit, motherboard. In late 80'ies the 8086/8088 was obsolete and the 286 processor was considered the slowest option in new PC's.
Because the 8086 (and 8088) is the first x86 CPU it is still popular under enthusiasts who like legacy hardware. With efficient programming it's possible to use the 8086 for a lot of tasks. Enthusiasts wrote programs to use FTP- and IRC-clients running on DOS, graphical web browsers and modified the original Wolfenstein 3D source code and let it run on the 8086. > Read more
Just like the 8088-clone but in 8086 version. The 8086 CPU's are almost identical except that they work with a 16-bit wide bus instead of 8-bit.
The production date of this chip is interesting. Intel designed the 8086 in 1976 and Kvazar made this CPU sixteen years later! At that time the Pentium was on the design table and both 386 and 486 systems were made for the masses. > Read more